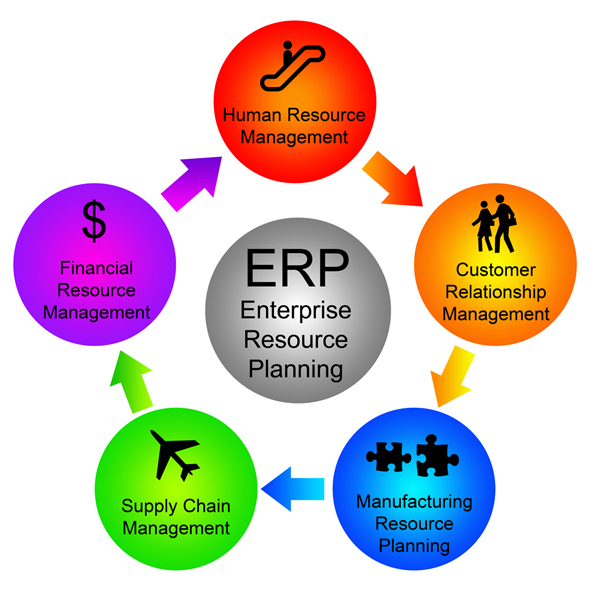
ERP is an acronym for enterprise resource planning, normally a system that is executed via software designed to improve the management of a business. Generally, ERP takes the form of a suite of applications that are then integrated in order to enable a company to collect and store data as well as manage and interpret it. ERP takes in many diverse functions including project planning, costing and development. The suite will normally also encompass product manufacturing and service delivery, sales and marketing, management of inventories, payment and shipping facilities.

Business benefits of ERP
Undoubtedly, ERP benefits entrepreneurs and business managers as it streamlines operations, centralizing data so that management has a more transparent view of corporate, as well as individual product or service, performance. As off-site cloud computing resources are mostly used, data can be collected and held in one place, rather than on a number of hard drives belonging to different employees or on several servers. Thus, there is one central database, which every department and relevant employee can access, thereby reducing the complications that can often arise from attempting to maintain all corporate data in a way that is consistent across various geographical locations or departments. A major advantage is that there is no longer any need to maintain separate accounting, logistics or warehousing databases.
Research and development (R&D)
Beyond up-to-date inventory and invoicing information, ERP has additional applications that are incredibly useful when it comes to scientific research and development. As researchers gather data over a period of time and store it in a database, so they can take advantage of analyzing and managing this “big data” – studying patterns in data usage and data sets and identifying anomalies or potential efficiencies. In fact, in analyzing ERP data, scientific researchers can get the help they need to create systems that will deliver solutions for actual data needs, rather than simply forcing existing data to conform to pre-defined systems.
Any type of scientific research that collects and analyzes data can use enterprise resource planning to achieve rapid and accurate data analytics. This is because it’s possible to select and separate required portions of data for analysis, thus enhancing the potential for the extraction of knowledge from data (data science). For example, organizations that conduct R&D, whether not-for-profit or for profit, find that ERP can help with key tasks such as achieving an overview of funders, setting up plans and associated budgets, managing the process of making funding applications, carrying out projects, monitoring progress and creating reports.
In the future, it seems highly likely that the contribution of data garnered from ERP will help to ensure that scientific research will factor in business interests when reaching important conclusions.

Customer testimonials
Enterprises that have used ERP have found that project management is greatly improved, as is transparency; so much so, in fact, that the introduction of ERP means that management is acutely aware of how a company is performing every step of the way and does not have to wait for post-event reports in order to judge progress.