The technology of smart clothing continually displays new innovations. The two most recent coming first by U.S. researchers, who created vibrant clothes that guide the blind people on the street and by Chinese scientists who built elastic yarn batteries embedded in clothing and feeding electricity. Approximately 285 million people suffer from impaired vision, according to the World Health Organization, and most, even in the most developed countries have no further help despite the typical white cane, which was invented in 1921.
The researchers of the company Tactile Navigation Tools, which was created by Doctor J. Rizzo’s from the Langone Medical Center of New York University developed clothes with electronic sensors that read the environment continuously and promptly notify the blind person who wears them. When an obstacle is around, the garment vibrates and the blind person is warned. The garment, in essence is a wearable device, named «Eyeronman» can be used by people with vision problems to help in orientation and in special circumstances, such as firefighters amid smoke, policemen, soldiers and others.
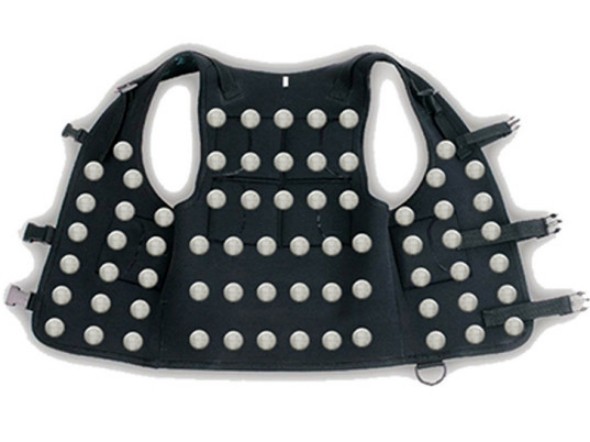

The Eyeronman is stocked with a wide range of sensors, including a system of lidar, a type of radar with laser used in autonomous vehicles even without a driver, ultrasound and infrared. The input data from the sensors are converted to the appropriate vibrations of the smart shirt, which is made from special type polymers. The garment detects all the obstacles around, i.e. within 360 degrees. Also researchers at Fudan University in Shanghai, created flexible lithium-ion batteries as much elastic yarns that can be woven into a garment and so incorporated in it.

Scientists originally built tiny wires of two carbon nanotubes, placed inside the other. Then the wires were coated with appropriate nanoparticles to create positive and negative poles of the battery, while added an electrolyte in a gel form. A section of ten centimeters of thread battery weighs just 0.08 grams and can illuminate a series of LED type lights for one minute. These elastic yarn batteries, which can be stretched up to 600%, are a source of electrical energy without the slightest containing metal. Although at present they have a small energy capacity and are relatively expensive to produce, as the wearable technology develops, such innovations are expected to see widespread applications.

By Nicole P.



